
New Technique Discovered For Easy Autism Detection in Kids
A new study has discovered a new technique that ensures autism spectrum disorder in kids is accurately and quickly detected by doctors. Previously discovered
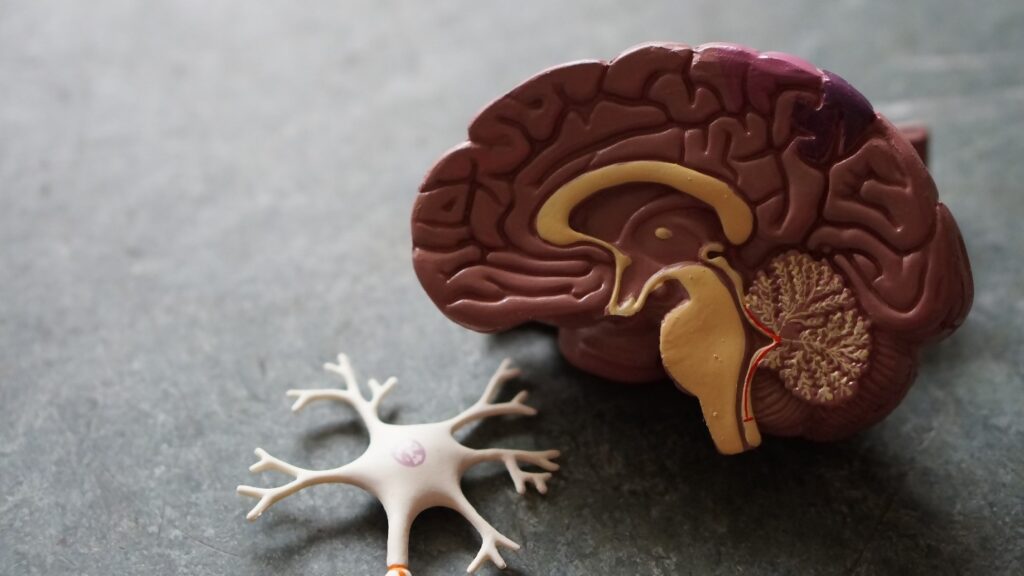
Researchers at the National Institutes of Health and UC San Francisco started working on a special variation of Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats (CRISPR). This variation (CRISPRi) allows them to better study the human brain and the diseases it can suffer from.
The researcher’s findings from this study are available in the journal Neuron. This article explains how the technique uses CRISPRi gene alternations together with cells that are stem-cell-derived. Together both techniques improve our knowledge of brain disease as they help scientist delve deeper into neural changes.
This advancement in brain disease research lets scientists target the genes without damaging the cell membrane. Such damages to cells made research impossible until now.
Scientist working on this task basically want to develop a CRISPR gene-editing device. Such technology helps stop cell membrane destruction during experiments. This advancement in neuroscience is only now possible because of recent technological breakthroughs.
Previous experiments failed at controlling the influence of the Cas9 enzyme. This enzyme is the main reason why neural cell membranes deteriorate in conventional experiments. That is why the new CRISPRi technology is so important as it cuts the gene without activating the enzyme.
Unlike the CRISPR-Cas9 technique that causes damage during experimentation, the new procedure builds on the previous mistakes and adapts them. That is why CRISPRi has the potential to change our understanding of genetic brain diseases. With the aid of this new technique, we can observe how the neuron cell reacts to genetic mutations. That is, we can observe the development of genetic disease up-close.
https://www.eurekalert.org/pub_releases/2019-08/uoc–tci081419.php

A new study has discovered a new technique that ensures autism spectrum disorder in kids is accurately and quickly detected by doctors. Previously discovered

New Study shows that different coloration of primates doesn’t indicate fertile phases, but individual characteristics and reproductive status. Previous studies of ornamentation in female primates

Today astronomers from the Event Horizon Telescope Project (EHTP) unveiled the first-ever picture of a black hole and I’m sure most of you will have

A new study reveals that acute kidney failure can be detected earlier than the previous and currently used methods in patients. Drug-induced acute kidney




DISCLAIMER: ConductScience and affiliate products are NOT designed for human consumption, testing, or clinical utilization. They are designed for pre-clinical utilization only. Customers purchasing apparatus for the purposes of scientific research or veterinary care affirm adherence to applicable regulatory bodies for the country in which their research or care is conducted.